AI, Agents, Workflows, LLMs - it all gets a bit confusing in today’s AI landscape around what all these mean. I want to break this down into a fairly simple framework to think about 4 distinct ways of using LLMs that get increasingly more complex.
1. Standalone LLM (Prompt in, Information Out)
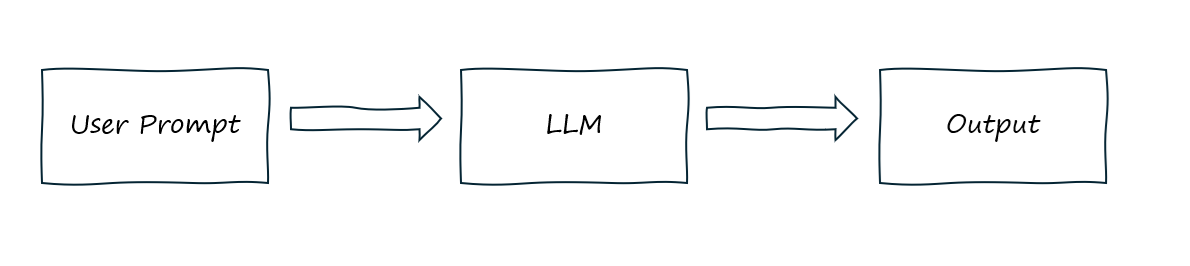
Standalone LLM
This is the simplest and easiest way to engage a LLM. You enter a prompt into an LLM and it will respond based solely on its training data and the input you gave it in the prompt. This is most useful when you want a quick, self-contained answer that doesn’t require up-to-date data, personalization, or external reasoning, e.g. summarizing a paragraph, rewriting text, generating titles, or writing social media copy. You can also give it in-prompt context to help improve the answers - a concept often referred to as one/few-shot learning.
Example Use Cases
- Copywriting assistant
- Text rewriting or summarization
- Code Snippets
| Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Simplicity and speed | No access to real-time data |
| Easy to embed in existing apps | Prone to hallucination |
| Low cost | Static behavior |
2. LLM + RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)
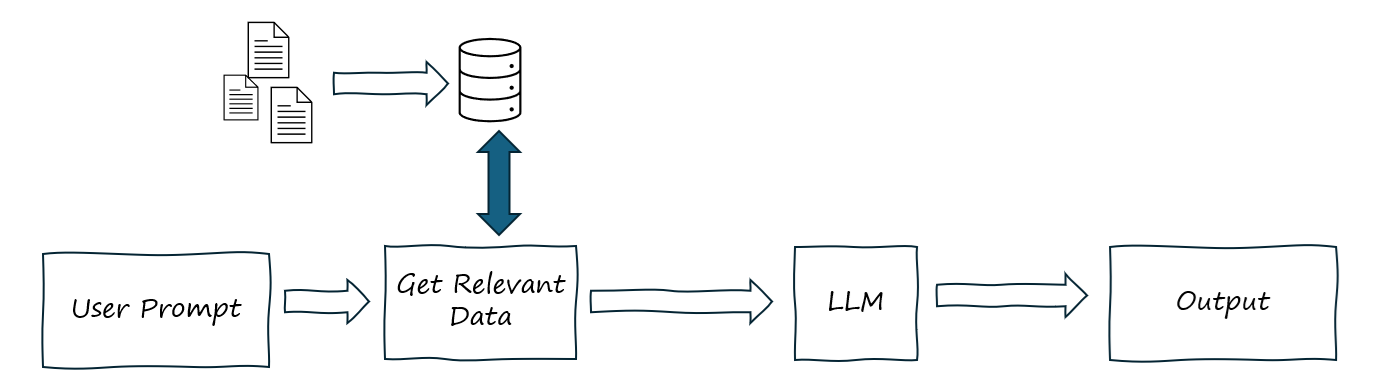
LLM + RAG
This takes the standalone LLM and augments it with external knowledge via a search or a database lookup. It often involves semantic search over vector embeddings representing the external knowledge you are augmenting the LLM with. Typically, the user enters a prompt, the prompt is parsed and used to search against a knowledge base where key pieces of information are retrieved and added to the prompt as context and this is all passed to a LLM to get a response. You can enhance your LLM responses with access to private datasets or even real time data. The bottleneck could be how well you approach the initial data retrieval.
Example Use Cases
- Internal policy chatbot
- Tech support assistant
- Document comparison and audit
| Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Access to real-time or custom knowledge | Requires proper data curation |
| Domain-specific accuracy | Retrieval quality is critical |
| Maintainable and update-friendly | Latency increases slightly |
3. AI Workflows (Orchestration of multiple tools and steps)
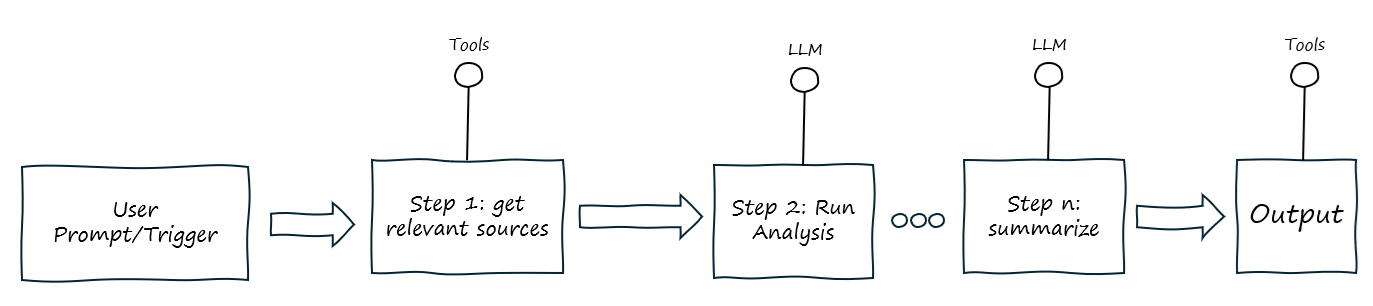
AI Workflow
Here we are getting more sophisticated workflows where a chain of tools or models are orchestrated. The tools can include APIs, code execution and decision trees etc and the LLM acts as a controller for different steps and services. Often you are looking at something like LangChain or Semantic Kernel to build this
Example Use Cases
- Document processing (OCR > parse > summarize)
- Multi-step customer interactions
- Lead qualification bot
- Onboarding assistant
| Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Structured and deterministic flows | Complex to build and maintain |
| Reusable building blocks | Higher latency |
| Better control over flow | Rigid logic |
4. AI Agents (Autonomous Decision-Makers)
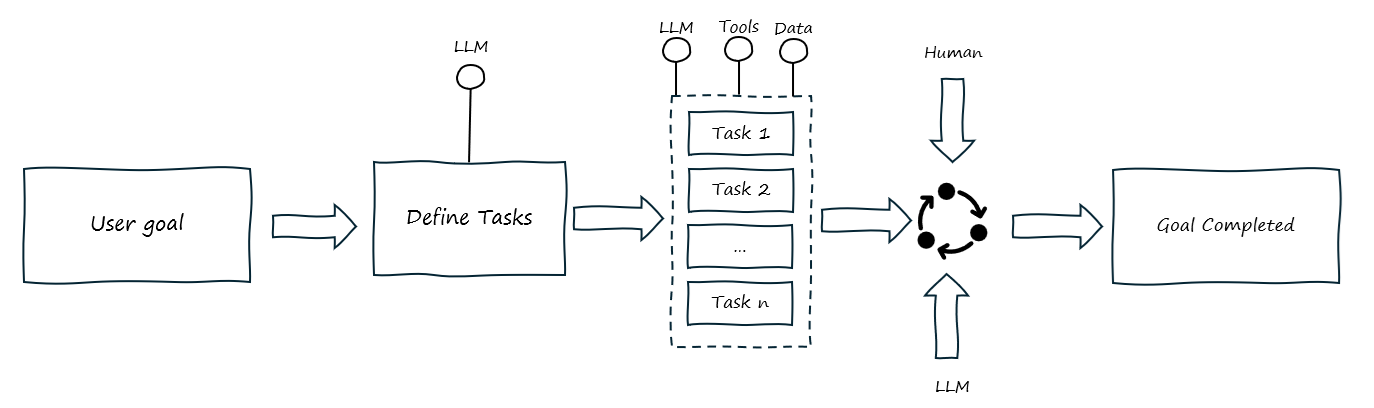
AI Agents
This is the most complicated of the workflows. Here you give the LLM a goal and it builds a plan, executes against that plan and achieves the goal. It often includes feedback loops, breaks the goal and plan down into tasks as well as figuring out which tools to access to help achieve the goal. The big difference between this and AI workflows is that AI agents work independently and define the workflows to execute where as with AI Workflow you will have predefined the workflow and steps to execute. This scenario provides a greater degree of autonomy and, in more complex agent scenarios, ai agents can evaluate output from different steps and redo them as appropriate.
Example Use Cases
- Customer service agents that escalate when needed
- Research assistants that look up and summarize sources
- DevOps bots that diagnose and resolve incidents
| Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Autonomy and adaptability | Unpredictable behavior |
| Can pursue complex, multi-step goals | Harder to debug and test |
| Long-term, multi-turn interactions | Resource intensive |
Each level adds complexity and capability. Not every task needs an agent, sometimes a simple prompt or RAG is enough so choose the right level based on your use case, perhaps even starting simpler and getting more complex as your needs grow.
Here are five high-impact example use cases that scale clearly across four stages of AI workflows: Standalone LLM > RAG > Workflow > Agent.
1. Virtual Financial Advisor
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| 🧠 Standalone LLM | “Explain what a Roth IRA is.” > LLM responds with generic financial explanation. |
| 📚 RAG | Pulls from latest IRS guidelines or your bank’s offerings to give accurate, personalized info. |
| 🧰 Workflow | Classifies user type (e.g., age, goals) > Pulls financial products → Suggests 3 best options with trade-offs. |
| 🤖 Agent | Agent tracks long-term financial goals, monitors market trends, recommends adjustments over time, and integrates with your bank accounts. |
2. Product Support and Troubleshooting Bot
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| 🧠 Standalone LLM | “My headphones won’t connect.” > Generic troubleshooting tips from LLM training. |
| 📚 RAG | Fetches the exact support article from your product documentation. |
| 🧰 Workflow | Diagnoses issue by walking through decision tree > Asks for serial number > Checks warranty API. |
| 🤖 Agent | Agent verifies issue, books repair appointment, initiates a return label, and follows up via email if unresolved. |
3. AI-Powered Content Marketer
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| 🧠 Standalone LLM | “Write a blog post about productivity tips.” > Generic, SEO-ish listicle. |
| 📚 RAG | Pulls in research or trends from your site’s analytics and industry news to customize the post. |
| 🧰 Workflow | Plan campaign > Generate blog + social posts > Schedule with calendar API. |
| 🤖 Agent | Runs A/B tests, analyzes engagement, re-optimizes future posts, and suggests campaign pivots autonomously. |
4. Healthcare Intake & Triage Assistant
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| 🧠 Standalone LLM | “What does a sore throat mean?” → General medical advice. |
| 📚 RAG | Pulls from medical knowledge base like Mayo Clinic, or your hospital’s triage guidelines. |
| 🧰 Workflow | Intake symptoms > Ask about history > Route to appropriate care path (e.g., telemedicine vs. urgent care). |
| 🤖 Agent | Tracks patient status over time, updates charts via EHR APIs, books follow-up, and reminds patient to take meds. |
5. Travel Planning Concierge
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| 🧠 Standalone LLM | “Plan a 3-day trip to Paris.” → Outputs a generic itinerary. |
| 📚 RAG | Pulls hotel, weather, and attraction info from external sources. |
| 🧰 Workflow | Chooses travel style > Finds best dates > Books hotel and flight via APIs > Outputs itinerary. |
| 🤖 Agent | Monitors weather, delays, or closures > Rebooks travel if needed > Sends real-time notifications > Optimizes entire trip on the fly. |